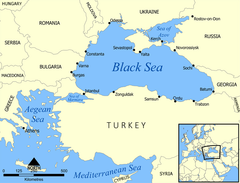
黒海
| 黒海 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 座標 | 北緯44度 東経35度 / 北緯44度 東経35度座標: 北緯44度 東経35度 / 北緯44度 東経35度 |
| 種類 | 内海 |
| 主な流入 | ドナウ川、ドニエプル川、リオニ川、南ブーフ川、クズルウルマク川、ドニエストル川 |
| 主な流出 | ボスポラス海峡 |
| 国 |
ブルガリア、ルーマニア、ウクライナ、ロシア, ジョージア、トルコ 部分的に承認された国家: アブハジア |
| 延長 | 1,175 km (730 mi) |
| 面積 | 436,402 km2 (168,500 sq mi) |
| 平均水深 | 1,253 m (4,111 ft) |
| 最大水深 | 2,212 m (7,257 ft) |
| 水量 | 547,000 km3 (131,200 cu mi) |
| 島 | 10以上 |



黒海︵こっかい︶は、ヨーロッパとアジアの間にある内海で、大西洋の縁海︵地中海 (海洋学)︶の一つである。マルマラ海を経てエーゲ海、地中海に繋がる。
バルカン半島、アナトリア半島、コーカサスと南ウクライナ・クリミア半島に囲まれており、ドナウ川、ドニエストル川、ドニエプル川などの東ヨーロッパの大河が注ぐ。アナトリアとバルカンの間のボスポラス海峡、マルマラ海、ダーダネルス海峡を通じて地中海に繋がっており、クリミアの東にはケルチ海峡を隔ててアゾフ海がある。
黒海に面する国は、南岸がトルコで、そこから時計回りにブルガリア、ルーマニア、ウクライナ、ロシア、部分的に承認された国家: アブハジア, ジョージアである。
黒海に面する有名な港湾には、イスタンブール︵ビュザンティオン、コンスタンティノープル︶から時計回りにブルガス、ヴァルナ、コンスタンツァ、オデッサ、セヴァストポリ、ヤルタ、ノヴォロシースク、ガグラ、バトゥミ、トラブゾン、サムスンなどがある。

地図中の青線︵バルト海上の紫線を含む︶が﹁ヴァリャーグからギリシ アへの道﹂を示す
ローマ帝国が衰亡し変質していく中、コンスタンティヌス1世は330年にローマ帝国の首都をローマからコンスタンティノープル︵現イスタンブール︶へと遷都する。395年のローマ帝国の東西分裂後は、コンスタンティノープルは東ローマ帝国の首都となり、人口数十万を擁する世界有数の大都市となっていった。コンスタンティノープルは短いボスポラス海峡を通じて黒海に直結しており、この大都市の出現により黒海交易はさらに盛んになった。東ローマ帝国自体も、黒海北岸の古いギリシア植民都市であるケルソネソス︵セヴァストポリ︶およびその付近のクリミア半島南岸を手中に治め、黒海を掌握していた。
650年頃、それまで西突厥の宗主権下にあったハザール・カガン国が独立し、カスピ海から黒海北岸を勢力下においた。ハザールはイスラム帝国とは敵対する一方、東ローマとは基本的に友好的な関係を維持した。またハザールは商業を保護し、バルト海からヴォルガ川を通ってカスピ海・黒海へと向かう、ヴァリャーグからギリシャへの道︵下記︶の西よりルートを活性化させ、またステップ・ルートの再活性化にも努めた。ハザールの黒海北岸支配は10世紀まで続いた。
9世紀前半以降、ヴァイキングの一派であるスウェーデン人︵ヴァリャーグ︶によって、﹁ヴァリャーグからギリシアへの道﹂と呼ばれるバルト海と黒海を結ぶ交易ルートが開設される。ルーシを貫き、ノヴゴロドからキエフを通りドニエプル川で黒海へと向かうこのルートは、ヨーロッパの南北を東側で結ぶ主要ルートとなり、キエフ大公国などのルーシ諸国家を東ローマ帝国と強く結びつけた。この時期に、東ローマの国教であるギリシア正教がロシアに受容されている。
第四次十字軍によって東ローマ帝国が一時滅亡すると、十字軍側のラテン帝国に付いたヴェネツィア共和国および、東ローマの後継国家であるニカイア帝国と結んだジェノヴァ共和国が古代ギリシャと同様の対遊牧国家の黒海交易へと進出し、1261年の東ローマ帝国復活後はジェノヴァが黒海交易を握り、ケルチ半島のカッファなどに植民地を築いた。
しかし、14世紀に入るとアナトリア半島に興ったオスマン帝国が勢力を拡大し、1453年にはコンスタンティノープルを落として東ローマ帝国を滅亡させ、コンスタンティノープル︵イスタンブール︶に首都を置いた。黒海とバルカン半島、アナトリア半島を繋ぐ要地に大帝国が本拠を置いたことで、これ以後黒海の制海権はオスマン帝国が握ることとなる。1475年には黒海北岸にあったモンゴル帝国北西分国ジョチ・ウルスの末裔、クリミア・ハン国を従属国とし、クリミア半島南岸に残っていたジェノヴァの植民地もオスマン帝国が直轄領としたことで、黒海はオスマン帝国の内海となった。

オデッサ市の象徴・ポチョムキンの階段。1841年に建設された。
この状況が変化するのは、露土戦争 (1768年-1774年)に勝利したロシア帝国が1774年のキュチュク・カイナルジ条約によってアゾフおよびケルチを獲得し、黒海北岸に橋頭堡を築いてからである。ロシアはそれまで首都サンクトペテルブルクほかわずかな港しか持っておらず、それも冬季にはすべて結氷するものであり、不凍港の獲得は悲願であった。この条約においてはロシアに黒海・地中海の自由航行権も認められ[7]、ここを足掛かりにロシアは黒海へ進出していく。
1776年にはセヴァストポリに黒海艦隊が設立され、1783年にはクリミア・ハン国を併合して、完全に黒海北岸を領土化した。ここにおいて、黒海はオスマンの内海から、ロシアとオスマンの海となった。
さらに露土戦争 (1787年-1791年)のヤッシー条約によってロシア領は黒海北西岸のエディサン地方に拡大し、この地にロシアは1794年にはオデッサ港を開港した。これにより外界への出口を獲得したロシアは、以後オスマン帝国を圧迫しながら徐々に南へと領土を広げていく。この政策は南下政策と呼ばれ、ロシア外交の根幹となるが、ロシアの強大化を恐れるヨーロッパ列強諸国はこれを認めず、オスマン帝国を支援する側に回った。この黒海の制海権争いも含むロシア・トルコおよび列強諸国間の対立は、東方問題と呼ばれて19世紀ヨーロッパ外交の焦点の一つとなる。
ロシアは露土戦争 (1828年-1829年)でも勝利を収め、1833年のウンキャル・スケレッシ条約によって完全に黒海の制海権を握った。しかし、イギリスなどがこれに反発して1853年にはクリミア戦争が勃発し、ロシアは破れ、1856年のパリ条約によって黒海は非武装化され、黒海艦隊も解体されて[8]この海域は中立化されることとなった。
しかし1871年、ロシアはパリ条約を改定させ、再び黒海艦隊を再建した。露土戦争 (1877年-1878年)の講和条約である1878年のサン・ステファノ条約によって、ロシアは黒海西岸を中心にさらに勢力圏を南下させたが、同年のベルリン条約によって一定の歯止めがかけられた。また、サン・ステファノ条約によってブルガリアがほぼ独立し、またベルリン条約によってルーマニアが北ドブロジャを得て黒海への出口を確保した。これにより、ルーマニアの海への出口となったコンスタンツァ港、ブルガリアの玄関口となったヴァルナ港・ブルガス港の整備がすすめられた。
ロシアの進出による黒海北岸の一元支配は、北岸の経済活性化をもたらした。一元支配によりこの地方での戦乱が止むと、もともと肥沃な北岸ステップ地帯には急速に入植が進み、ロシア最大の穀倉地帯となっていった。オデッサ港はロシアの南の玄関口となり、黒海沿岸の肥沃な農地から採れる穀物の輸出港として栄えた[9]。また、オデッサ港やロシア中央部から鉄道が延伸され、ドンバス地方の炭田やクリヴォイログの鉄鉱石を基にして、製鉄をはじめとする工業化がウクライナ北東部で急速に進んだ。
名称[編集]
日本語では専ら黒海︵こっかい︶と呼ばれる。英語ではBlack Sea、トルコ語ではKaradeniz、ロシア語ではЧёрное море、ウクライナ語ではЧорне мореとなる。トルコ語のKara Denizには﹁偉大なる海﹂という意味の他に﹁黒い海﹂という意味もあり、ちなみに地中海はトルコ語でアク・デニズ︵白い海︶という。名称の変遷[編集]
ギリシア神話の時代には、黒海沿岸などギリシアより北方の未開地に女性だけの部族アマゾンがいて、黒海もかつてアマゾン海と呼ばれた。現にトルコ沖にはアマゾン島がある。 古く︵紀元前700年頃 - 500年頃︶は、古代ギリシア語でἌξεινος Πόντος (Axeinos Pontos︵ポントス・アクセイノス。暗い、薄暗い海[1]。愛想が悪い海。)、ラテン語でPontus Euxinus︵ポントス エウクセイノス。客人を歓待する海、客あしらいのよい海。︶[2]と呼称されていた。ギリシャ人が進出し、自分たちの勢力圏とすることで、前者が後者に変わった、とされる。東ローマ帝国の文書内ではPontos︵ポントス︶とだけ記述されている場合が多い︵ギリシア語で﹁海﹂の意︶。 中世︵500年頃 - 1500年頃︶には、イタリア語文献ではMare Maggiore︵Greater Sea、偉大なる海︶という名称が用いられ、アラブの文献では多数の名称︵ローマの海、偉大なる海、トラブゾンの海、等︶が用いられている。 オスマン帝国期︵1500年頃 - 1700年頃︶には、オスマン帝国初期にトルコ語でKara Deniz︵黒い海︶という名称が文献に現れ始める。 ロシア帝国期︵1700年頃 - 1860年︶には、Чёрное море︵Chernoe More、黒い海︶という名称が用いられている。 1860年以降になると、Black Sea︵黒海︶という英語の呼称が国際的に使われるようになった。概要[編集]
面積は436,400km2ある。最大水深は2,206m。名称は黒味を帯びた海水に由来し、この黒味の原因は硫化鉄であるとする説と、地中海よりも豊富な微小藻類であるとする説がある。前者は次のように説明される。黒海は、大陸に囲まれた海であり、地中海と辛うじて結ばれているだけの閉鎖性水域である。黒海の海水は水深200mを境として冷たく塩分の薄い表層水︵河川から流入し、地中海へ流出︶と、暖かく塩分の濃い深層水︵地中海から流入︶が層を成して混合しない。このため深層水では酸素が欠乏し嫌気性バクテリアによって硫化水素が発生し、海水中の鉄イオンと結合し黒色の硫化鉄を生成する。表層水は充分な酸素を含むため豊かな生態系を擁しており、漁業も行われている。漁獲高は年25万トンから30万トンに上り、その3分の2がアンチョビで、残りはアジやイワシ、ニシンやチョウザメなどである[3]。 気候は、南西部が地中海性気候、北端のドニエプル川河口付近がステップ気候であるほかは、ほぼ全域が温暖湿潤気候である。 北東岸には砂州が多く発達し、最も長いものではオデッサやドニエプル川の西からクリミア半島近くまで130kmにもわたって延びているものがある。クリミア半島は東部で細いケルチ海峡によりそれ以東と分離されているが、北側も大陸とそれほど確固とした繋がりがあるわけではなく、黒海と、アゾフ海とつながる腐海の間は、幅5km程度のペレコープ地峡によって繋がっているに過ぎない。北東岸、とくにウクライナ領内の海岸は平坦で、大平原の広がる穀倉地帯となっているが、クリミア半島南岸近くにはクリミア山脈が伸びており、海岸線近くまで山が迫っている。これは北西岸も同様で、コーカサス山脈が北西から南東に延びており、海岸平野はさほど広くない。南岸のアナトリア半島でも、海岸沿いにポントス山脈が東西に延びており、平原の発達はあまりない。 黒海に注ぎ込む河川のうち最大のものは、西岸、ルーマニア・ウクライナ国境で流れ込むドナウ川である。次いで、同じく北西岸に流れ込むドニエストル川、北岸に流れ込むドニエプル川が大きなものである。これ以外は、南岸、アナトリア半島の中部から流れ込むクズルウルマク川を除き、大河と呼べるものはほとんどない。 黒海はそれ自体が重要な交通路となっているほか、流れ込む河川交通との連結運輸も重要となっている。ドン川からはヴォルガ・ドン運河を通してヴォルガ川やカスピ海と結ばれ、さらにヴォルガ川からはヴォルガ・バルト水路を通じてバルト海と、さらにその途中のラドガ湖で白海・バルト海運河によって白海まで内陸水運のみで繋がれている。また、西ではドナウ川からライン・マイン・ドナウ運河を通じてマイン川・ライン川へ、さらに北海へと結ばれている。歴史[編集]
南西にイスタンブールがあり、古くから東ローマ帝国、オスマン帝国の首都があったことから、黒海地域の歴史は複雑である。オスマン帝国時代には対ウクライナなどの黒海貿易もあった[4]。黒海が位置するのがアジアとヨーロッパの境界線上であるため、中東史、ヨーロッパ史、ロシア史のどの分野でも記述される機会が少なかったが、少しずつ黒海周辺を一つの地域として黒海歴史研究をする学者が出てきている[5]。古代[編集]
紀元前7世紀頃から、ボスポラス海峡を通ってギリシャ人が黒海沿岸各地に植民を始め、タナイスやパンティカパイオン、オルビアといった植民市が各地に建設されていった。これらの植民市は北の草原地帯に住むスキタイ人やサルマティア人らの遊牧国家から彼らの支配地の黒海沿岸黒土︵チェルノーゼム︶地帯の農耕民から徴税した穀物や戦争捕虜の奴隷を購入し、ぶどう酒や武器などのギリシャの産物とを取引して力を付けていった。また、これらの植民諸都市、とくにタナイスは東西交易路の一つ、ステップ・ルート︵草原の道︶の西端にも当たっており、黒海はこの頃にはすでに東西交易の重要なルートとなっていた[6]。 スキタイ人の手により東方の産物が植民都市に持ち込まれ、ギリシャ人によって地中海世界へと運ばれていった。この交易の様子はヘロドトスの﹁歴史﹂にも描かれている。そして紀元前5世紀にはこれらの植民市を統合してボスポロス王国が成立し、穀物などの貿易を基盤にして国力をつけていった。ボスポロス王国はのちにローマ帝国の従属王国となりつつ4世紀頃まで存続したが、フン族によってほぼ滅ぼされた。紀元前1世紀にはいると、ポントス王国など黒海南岸の諸国はすべてローマ帝国の領域となり、ローマの勢力圏となった。中世[編集]

近代[編集]

現代[編集]
第一次世界大戦が勃発すると、黒海ではロシアとオスマン帝国海軍・ドイツ帝国海軍との間で激しい戦闘が数度行われた。1917年、ロシア革命によってロシア黒海艦隊は数度所属を変えることとなり、最終的に1920年にソヴィエト連邦の管轄下に入るものの、この間主要艦船は国外に脱出し、黒海艦隊は壊滅状態となった。1920年、大戦に敗北したオスマン帝国はセーヴル条約によって、黒海の出口にあたるボスポラス海峡・マルマラ海・ダーダネルス海峡とその周辺地域は国際機関﹁海峡委員会﹂の管理下に置かれることとなったが、この条約に反発したムスタファ・ケマルが他国軍を追い払い、1923年に締結されたローザンヌ条約では海峡の自由通行は認められたものの、海峡管理権はトルコ共和国のものとなった。 さらにトルコは条約の改正を求め続け、1936年のモントルー条約によって商船の自由通行と軍艦の通行制限が認められ、これによって黒海沿岸諸国の地中海進出は再び阻まれた。ソヴィエト連邦が成立すると黒海艦隊は再建・増強されたものの、1941年に始まる黒海の戦いにおいて黒海艦隊はドイツの航空機の前に劣勢を強いられた。第二次世界大戦後には黒海艦隊はみたび再建され、黒海は﹁ソ連の海﹂となった。 また、貿易上も黒海はソ連にとって非常に重要であり、輸出の半分、輸入の4分の1は黒海経由で行われていた[10]。しかし、黒海の出口はモントルー条約のもとアメリカ寄りのトルコ政府が押さえており、ここから地中海方面へソ連が進出することは困難だった。 1991年のソ連の崩壊により、黒海北岸はほとんどが新たに独立したウクライナに、東岸はやはり新たに独立したジョージアに属することとなり、ロシア領は北東部のみへと大幅に縮小した。これらの新独立国を包含する新たな国家間機構の必要性が高まり、1992年にはトルコの主導により沿岸諸国によって黒海経済協力機構が結成された。このほか、2001年にはやはりトルコ提唱により黒海海軍合同任務群が設立された。 しかし、とくに北岸のロシアとウクライナの間はしっくりいっておらず、黒海艦隊の所属やクリミア半島の帰属などで対立が続いた。2007年には、ロシア・ウクライナガス紛争を避けてウクライナを迂回し、黒海のトルコ領海内を通ってロシアとヨーロッパを結ぶパイプライン、サウス・ストリーム計画が発足した。ロシアは2008年の南オセチア紛争でジョージア海軍を壊滅させると、2014年にはウクライナの騒乱に乗じてクリミア編入を一方的に宣言し︵2014年クリミア危機︶、ソ連崩壊後にウクライナに移管されていた艦艇も取り戻して崩壊前の戦略的状況をほぼ回復した。沿岸主要都市[編集]
| 黒海沿岸の人口の多い10都市 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 順位 | 都市 | 国 | 州・郡 | 人口 | ||||||
| 1 | イスタンブール | トルコ | イスタンブール県 | 13,624,240[11] | ||||||
| 2 | オデーサ | ウクライナ | オデーサ州 | 1,003,705 | ||||||
| 3 | サムスン | トルコ | サムスン県 | 535,401[12] | ||||||
| 4 | ヴァルナ | ブルガリア | ヴァルナ州 | 474,076 | ||||||
| 5 | セヴァストポリ | ウクライナ(ロシアが占領中) | セヴァストポリ連邦市 | 379,200 | ||||||
| 6 | ソチ | ロシア | クラスノダール地方 | 343,334 | ||||||
| 7 | トラブゾン | トルコ | トラブゾン県 | 305,231[13] | ||||||
| 8 | コンスタンツァ | ルーマニア | コンスタンツァ県 | 283,872[14] | ||||||
| 9 | ノヴォロシースク | ロシア | クラスノダール地方 | 241,952 | ||||||
| 10 | ブルガス | ブルガリア | ブルガス州 | 223,902[15] | ||||||

政治[編集]
地政学観点で黒海を考える時に、北のウクライナ、南のトルコ、東のジョージアは、欧州を代表する国際機構、NATO︵トルコは加盟︶、EUへの加盟を目指しつつも実現できていない国々であり、また海を介した交流・協力・対立の歴史から、近年﹁黒海地域﹂という黒海周辺国家を一つの地域としてとらえる研究が増えている。上記の国々が所属する国際機構、黒海経済協力機構 (BSEC) やGUAM︵トルコはオブザーバー︶は、最終的な目標として﹁欧州統合﹂を掲げている点が共通している。EUもまたルーマニアとブルガリアがNATOとEUに加盟したことから、その領域が黒海沿岸に到達し、安全保障及び将来の欧州統合プロセスを考える際に黒海地域に対する包括的な政策の必要に迫られていた。その結果、﹁黒海シナジー﹂や﹁東方パートナーシップ﹂などの地域イニシアチブを開始し、地域諸国との協力関係を模索している。そして、欧州とは何か、すなわち﹁ヨーロッパ性 (Europianity)﹂とは何かを考える際に、黒海地域をどのように理解するかが重要となりつつある[5]。経済[編集]
黒海はボスポラス海峡・ダーダネルス海峡を通じて地中海に通じ、さらに地中海からジブラルタル海峡を通じて大西洋へ、スエズ運河を通じて紅海からインド洋へと抜けることができ、ユーラシア大陸の奥深くに食い込んだ外洋の先端部に位置するため、周辺諸国にとって貴重な海運ルートを提供している。ブルガリア、ルーマニア、ウクライナ、ジョージアにとっては唯一の海洋であり、またロシアにとっても黒海沿岸は不凍港として、また南部の玄関口として、非常に重要である。 ソビエト連邦崩壊以降、東のカスピ海沿岸地域での石油開発が盛んになったため、カスピ海から最も近い外洋である黒海への石油積み出しが盛んに行われるようになった。カスピ海からの石油パイプラインは従来すべて北のロシア方面へと走っていたものの、カスピ海の石油産出が増加するにつれ黒海沿岸へのパイプライン建設の必要性が叫ばれるようになり、まず1997年、それまで﹁ノヴォロシースクからバクーへと﹂走っていたパイプラインを改修し、﹁バクーからノヴォロシースクへ﹂走るパイプラインが建設された。ついで1999年、バクーから黒海沿岸のジョージア・スプサ港へのパイプラインが建設された。このルートは陸上距離が短く、建設・輸送コストが抑えられるうえロシアを経由しないため利用価値は高かったが、パイプラインとしては小規模なものだった。ついで、2001年にはカザフスタンのテンギス油田からのCPCパイプラインがノヴォロシースクまで建設され、黒海は重要な石油輸出ルートとなった[16]。 しかし、黒海と地中海を結ぶボスポラス・ダーダネルス両海峡は非常に幅が狭く、石油輸出船の急増により船舶通航量は限界に達しつつあった。2004年にはトルコが両海峡のタンカー通行規制を強化し、その結果タンカーが黒海にて滞留する事態となった[17]。このため、黒海を通らない石油ルートがふたたび模索され、2006年にはバクーからジョージア内陸部・トルコ東部を通り、トルコ領南東部にあって地中海に面するジェイハン港へと直接抜けるバクー・トビリシ・ジェイハンパイプライン︵BTCパイプライン︶が開通し、これにより黒海の石油輸出に占める重要性は死活的なものではなくなった。観光[編集]



地質と海底地形[編集]
黒海の成因は白亜紀の火山弧が分離したことと新旧テーチス海の沈降によるところが大きいが、それらの時期については議論がある[20][21]。形成初期から圧縮力が働き盆地として沈降したが、火山活動と造山運動も無数に生じ、コーカサス、クリミア、バルカンなどの山地が形成された[22]。 現在も続くアフリカプレートとユーラシアプレートの衝突と、北および東アナトリア断層に沿ってアナトリア地塊が西へ動くことが、黒海を沈降させアナトリア地域で火山が活発化する原因である[23]。これら地質メカニズムが長期にわたって黒海を他の海洋から隔離したと言える。今の海底地形の特徴としてクリミア半島から南に延びる盛り上がった部分が作る浅い陸棚があり、190kmの広がりを見せる。黒海の中央部は嫌気性の深海平原で最大水深はヤルタの南で2,212mになる[24]。関連書籍[編集]
- チャールズ・キング 『黒海の歴史』 明石書店、2017年4月。ISBN 4750344745。
脚注[編集]
(一)^ (キング 2017)、p14。同箇所では、ギリシア語名称は、より古いイラン語から借用された可能性を指摘している。
(二)^ (キング 2017)、p14
(三)^ 山本ほか 1994, p. 180.
(四)^ ﹁オスマン帝国−イスラム世界の﹁柔らかい専制﹂−﹂鈴木董著︵講談社、1992︶
(五)^ abCharles King"The Black Sea: A History", Oxford University Press, 2004
(六)^ 長澤和俊﹃シルクロード﹄p72-73 講談社学術文庫、1993年 ISBN 4061590863
(七)^ 黛秋津 ﹃第1章 帝国のフロンティアとしてのカフカース﹄p34 彩流社︿﹃カフカース―二つの文明が交差する境界﹄所収﹀、2006年。ISBN 978-4779112157。
(八)^ ﹁図説 ロシアの歴史﹂p92 栗生沢猛夫 河出書房新社 2010年5月30日発行
(九)^ 黒川祐次 ﹃物語ウクライナの歴史 : ヨーロッパ最後の大国﹄p158 中央公論新社︿中公新書; 1655﹀、東京、2002年︵日本語︶ISBN 4-121-01655-6。
(十)^ 山本ほか 1994, p. 179.
(11)^ “Turkish Statistical Institute”. Rapor.tuik.gov.tr. 2016年1月16日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2014年1月14日閲覧。
(12)^ “Turkish Statistical Institute”. Rapor.tuik.gov.tr. 2012年12月21日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2014年1月14日閲覧。
(13)^ “Turkish Statistical Institute”. Rapor.tuik.gov.tr. 2014年1月14日閲覧。
(14)^ Stiati.ca. “Cele mai mari orase din Romania”. Stiati.ca. 2013年2月19日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2014年1月14日閲覧。
(15)^ “Turkish Statistical Institute”. Rapor.tuik.gov.tr. 2013年4月18日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2014年1月14日閲覧。
(16)^ 輪島 2008, p. 23.
(17)^ 輪島 2008, pp. 42–43.
(18)^ 田辺・竹内 2011, p. 174.
(19)^ 田辺・竹内 2011, p. 107.
(20)^ McKenzie, DP (1970). “Plate tectonics of the Mediterranean region”. Nature 226 (5242): 239–43. Bibcode: 1970Natur.226..239M. doi:10.1038/226239a0. PMID 16057188.
(21)^ McClusky, S., S. Balassanian, et al. (2000). “Global Positioning System constraints on plate kinematics and dynamics in the eastern Mediterranean and Caucasus”. Journal of Geophysical Research 105 (B3): 5695–5719. Bibcode: 2000JGR...105.5695M. doi:10.1029/1999JB900351.
(22)^ Shillington, Donna J.; White, Nicky; Minshull, Timothy A.; Edwards, Glyn R.H.; Jones, Stephen M.; Edwards, Rosemary A.; Scott, Caroline L. (2008). “Cenozoic evolution of the eastern Black Sea: A test of depth-dependent stretching models”. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 265 (3–4): 360–378. Bibcode: 2008E&PSL.265..360S. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.10.033.
(23)^ Nikishin, A (2003). “The Black Sea basin: tectonic history and Neogene–Quaternary rapid subsidence modelling”. Sedimentary Geology 156: 149–168. Bibcode: 2003SedG..156..149N. doi:10.1016/S0037-0738(02)00286-5.
(24)^ Remote Sensing of the European Seas. (2008). p. 17. ISBN 1-4020-6771-2




