原子時計

原子時計︵げんしどけい、英: atomic clock︶は、原子や分子のスペクトル線の高精度な周波数標準に基づき最も正確な時間を刻む時計である。高精度のものは10−15︵3000万年に1秒︶程度、小型化された精度の低いものでも10−11︵3000年に1秒︶程度の誤差である。
原子時計に基づく時刻系を原子時と呼ぶ。現在のSI秒および国際原子時︵英: International Atomic Time︶は原子時計に基づく。
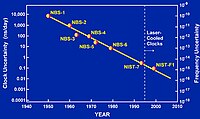
原子時計の精度の向上。縦軸は一日当りの誤差︵ナノ秒︶、横軸は西暦 を表す。NIST-F1ではレーザー光によって原子の熱運動を低減することで精度を上げている︵レーザー光冷却︶
原子や分子はスペクトル吸収線・輝線︵決まった周波数の電磁波を吸収・放射する性質もしくはその周波数︶を持ち、水晶振動子などよりも高精度な周波数標準となる。周波数は時間の逆数であるから、時間を高精度で測定できる。SI秒の定義もこの性質を利用している。
原子時計は、このような周波数標準器と超高精度の水晶振動子によるクォーツ時計とを組み合わせ、その水晶振動子の発振周波数を常に調整・修正する仕組みによって実現される。
原子時計を元に作られた正確な時刻情報は標準電波として放送されており、その電波を受信してクォーツ時計の誤差を修正しているのが電波時計である。
原子時計には、次のような様々なタイプがある[1]。
●マイクロ波時計 ︵例︶セシウム原子時計︵現在の秒の定義となっている。︶
●光原子時計
●単一イオン時計 ︵例︶ストロンチウムイオン時計、イッテルビウムイオン時計
●中性原子光時計
●旧型︵自由空間のもの︶ ︵例︶カルシウム時計、マグネシウム時計
●新型︵束縛されている︶ ︵例︶ストロンチウム光格子時計、イッテルビウム光格子時計

1984年から1993年まで国際原子時の校正に使われていたセシウ ム原子時計の共振部。国立科学博物館の展示。
マイクロ波時計の一種である。アンモニアやセシウムの他にルビジウムや水素なども用いられるが、セシウム原子時計の例について述べる。まず炉から放射されたセシウム133の蒸気を、磁場によって超微細準位の異なる2つに分離する。分離されたうち基底状態の原子に水晶振動子を基準として 9192631770 Hz のマイクロ波を照射し、これによって励起された原子に再び磁場をかけて分離する。励起状態のセシウムの量が多くなるよう周波数を調整し、正確な 9192631770 Hz のマイクロ波を作り出す。1967年から、国際的な1秒の定義となっている。誤差は1億年に1秒︵10−15︶程度とされている。最高精度を実現しているのは1次標準の数台に限られており、多くは少し精度の低い商業的に作られた2次標準を用いている。

NISTの2013年のイッテルビウム光格子原子時計。
レーザーを使って原子を光格子に捕捉するアイデアはロシアの物理学者Vladilen Letokhovによって1960年代に提唱された[3]。原子時計の脱進機のためのマイクロ波から光波︵計測はより難しいが性能はより高い︶までの波長域についての理論はジョン・ホールとテオドール・ヘンシュによって開拓され、2005年にノーベル物理学賞を受賞した。2012年にノーベル物理学賞を受賞したデービッド・ワインランドは高い安定性の時計を開発するための捕捉された単一イオンの性質を探求したパイオニアであった[4]。最初の光時計はNISTのJun YeやAndrew Ludlowによってストロンチウムを用いて2000年に開発が始められ、2006年に発表された[5]。
フェムト秒周波数コムと光格子の開発は原子時計を新世代へと導いた。これらの時計はマイクロ波よりも可視光を放出する原子遷移に基づいている. 光時計の開発の主な障壁は光周波数の直接計測の困難さにある。この問題はフェムト秒周波数コムと呼ばれる自己参照型モード同期レーザーによって解消された, 2000年に周波数コムが開発される以前は、テラヘルツ技術が電波と光周波数のギャップを埋めるために必要とされていたが、そのシステムは煩雑なものだった。しかし、周波数コムが洗練されたことで、この計測の可用性は大幅に上がり、世界各地で数々の光時計が開発される道を開いた[6]。
電波の波長域では、吸光分光法が発振器︵この場合レーザー︶を安定させるために用いられる。光の周波数がフェムト秒コムを用いて可算的な電波周波数に分割される際、位相ノイズの帯域幅も同じ因子によって分割される。レーザー位相ノイズの帯域幅は安定なマイクロ波源よりも一般的に大きいが、分割後にはより小さくなる[6]
光周波数を用いた原子時計の主要な標準システムは以下のものがある:
●イオントラップ中に隔離された単一イオン;
●光格子中に捕捉された中性原子[7][8]
●三次元量子気体の光格子中に充填された原子群[9]
これらのテクニックは原子やイオンを外部の雪道から高度に隔離し、非常に安定な周波数基準を実現する[9][10]。レーザーおよび磁気光学トラップを用いて原子を冷却することで、精度の向上が得られる[11]。
捕捉原子の候補としては、Al+, Hg+/2+,[7] Hg, Sr, Sr+/2+, In+/3+, Mg, Ca, Ca+, Yb+/2+/3+, Yband Th+/3+.[12][13][14]がある。原子時計の電磁放射線の色はシミュレートされた元素に依存する。例えば、カルシウム光時計は赤色光が産出された際に共鳴し、イッテルビウム光時計は紫色光で共鳴する[15]。
原理[編集]

セシウム原子時計[編集]

その他の原子時計[編集]
●水素メーザ原子時計 - 測定時間1秒で10−13、1000秒で10−15 ●ルビジウム原子時計 - 測定時間1秒で10−11、1000秒で10−13 ●イッテルビウムイオン原子時計 - 測定時間1秒で 10−12.5、1000秒で 10−13.5[2]光格子時計[編集]

ストロンチウム光格子時計[編集]
レーザー光の干渉定在波によって作られた光格子の中に、ストロンチウム原子約100万個をラム・ディッケ束縛により閉じこめる︵原子間相互作用を排除することにより、単一原子時計100万台と等価︶。光格子に閉じ込めるために原子を数μKまでレーザー冷却する。ラム・ディッケ束縛によりドップラーシフトおよび反跳シフトの影響を排除できる。さらに、光格子を構成するレーザーの波長を適切に選定する︵魔法波長︵~800 nm︶あるいは魔法周波数︵~375 THz︶と称する︶ことにより、ストロンチウム原子の時計遷移の基底状態および励起状態における光格子レーザーに起因するエネルギー準位のシフト︵光シフトと称する。その量は時計遷移の基底状態、励起状態の両者において、光格子レーザー周波数 320〜420 THz に対し遷移周波数換算 −100〜−200 kHz 程度︶の差[注 1]をほぼゼロとすることが出来るため、光シフトの影響が極めて少ない︵魔法周波数を9桁の精度で決めてプロトコルとして共有し、18桁の計時精度を実現する︶。2001年東京大学の香取秀俊[16]︵2011より理化学研究所主任研究員兼務︶によって提唱され[17]、2003年に基礎実験に成功[18]し、2005年に開発に成功[19]した。セシウム原子時計を超える原子時計として期待されている[20][21]。﹁周波数コム﹂︵光周波数コム。レーザー光を利用して光の周波数を精密に測定する仕組み︶を使い、より高い周波数︵マイクロ波ではなく光波︶の使用により安定度を上げる。 理論的にはセシウム原子時計の1000倍の﹁300億年に1秒﹂の精度がある。2009年現在16桁の精度が実現している︵429228004229873.7 Hz︶。2006年10月の国際度量衡委員会で、﹁秒﹂の二次表現︵秒の新しい定義の候補︶として採択された[22]。 2013年[23]、香取はストロンチウム原子分光︵中空フォトニック結晶ファイバ中︶に成功した。共鳴周波数幅は 7.8 kHz であった[24][25]。 2015年2月、香取、高本将男らは、ストロンチウム光格子時計2台を比較することにより、10−18前半の精度を確認したと発表した[26][27]。イッテルビウム光格子時計[編集]
ストロンチウム光格子時計をしのぐ精度をもつ可能性のあるものとして、イッテルビウム171光格子時計の開発が進んでいる。産業技術総合研究所計測標準研究部門時間周波数科の洪鋒雷・研究科長、安田正美・主任研究員らの開発による。黒体輻射や核スピンの影響が少なく精度が高いと考えられている。2010年現在の周波数は、518295836590864±28 Hz︵2009年測定、60万年に1秒ずれる精度︶である[28]。その後、装置の改善などを行い、2012年現在の周波数は、518295836590863.1±2.0 Hz︵2012年測定、相対不確かさ=3.9×10-15︶[29]。2012年10月の国際度量衡委員会で、秒の二次表現︵秒の新しい定義の候補︶として採択された[30]。歴史[編集]
1949年、アメリカ国立標準局においてアンモニアの吸収線を用いた原子時計が物理学者ハロルド・ライオンズによって発明された[31][32]。またアメリカで発明され、イギリス国立物理学研究所︵NPL︶のルイ・エッセンらによって開発されたセシウム原子時計は1955年から1958年まで国際原子時︵TAI︶を刻み実用化第1号となった。その後、1967年の第13回国際度量衡総会において現在用いられている国際単位系︵SI︶の秒の定義﹁セシウム133の原子の基底状態の2つの超微細準位の間の遷移に対応する放射の周期の 9192631770 倍に等しい時間﹂[33]が決定された。1991年12月にヒューレット・パッカードが発表したセシウム原子時計HP 5071Aの誤差は160万年に1秒としてギネスブックに﹁最も正確な時計﹂として認定されていた[34]。2011年8月の発表によると情報通信研究機構︵NICT︶と東京大学が独立に開発した原子時計を超高精度光伝送技術を用いて結び、6500万年に1秒︵16桁︶の精度を確かめた[35][36]。米国には70億年に1秒の精度とされる原子時計がある[37]。閏秒[編集]
原子時計が進歩したため、地球の自転による一日の長さ︵LOD‥Length of Day︶を正確に計測することが可能になった。1秒の長さは、1820年頃のLODに基づいて定義されていたために、セシウム原子の遷移の歩度︵9192631770周期︶による秒の定義とは合わなくなった。そのため何年かに1回閏秒を挿入して時間調整をしている。詳細は「閏秒#1日の長さ LOD」および「閏秒#閏秒挿入の理由についての誤解」を参照
利用[編集]
この節は言葉を濁した曖昧な記述になっています。 |
●高精度の時計を一番に必要としているのは長さの計測である。長さを正確に測るためには、正確な時計が必要である。現在ではレーザー波で、正確に長さが測れる︵以前は白金・イリジウム合金製の標準メートル原器を元にしていたため、温度や摩耗の問題があった︶。
●また電波において、正確な周波数同調が出来るようになった。
●時間、長さ、周波数の3つは重さや電気を正確に測るために必要である。
●GPS衛星には原子時計を搭載して、正しい位置を表すための正確な電波を出す。
●Googleなどの国際的にサービスを行う企業や、カレンダー、時刻サービスを提供する企業では正確な時計が必要である。そのため各国データセンターには原子時計が置かれている。[38]
将来[編集]
この節は言葉を濁した曖昧な記述になっています。 |
●時計の精度が上がると相対性理論により時計がある場所の速度・重力・電磁場が精度に大きく関係してくる︵セシウム原子時計でも地球上と人工衛星軌道での時間の進む速さの違いが検出される︶。逆に考えると、電磁場や重力場︵重力波?︶︵時空のゆがみの検出︶を高精度で測定できる可能性を秘めている。
●物理学の基本量︵光速c、プランク定数h、素電荷e、万有引力定数G、微細構造定数αなど︶を正確に決定できる。これらの数字のつながりが解明される可能性がある。
●相対性理論と量子力学の2つは根本の部分で分かっていなかったり、微妙に整合性がとれていない。どちらが正しいかわかるようになり、統合・調整できる可能性がある。
脚注[編集]
注釈[編集]
出典[編集]
(一)^ 安田正美、"1秒って誰が決めるの? 日時計から光格子時計まで"、p.99の図による、ちくまプリマー新書、筑摩書房、2014年6月10日 初版第一刷、ISBN 978-4-480-68918-4
(二)^ 新しい高精度マイクロ波原子時計の開発・試作に成功〜汎用的なルビジウム原子時計の約5倍の精度を実現〜 情報通信研究機構 2014年8月20日
(三)^ sarah.henderson@nist.gov (2020年9月29日). “Optical Lattices: Webs of Light” (英語). NIST. 2022年2月14日閲覧。
(四)^ “The Prize's Legacy: Dave Wineland”. NIST.gov. NIST (2017年3月3日). 2022年2月11日閲覧。
(五)^ “Optical Lattices: Webs of Light” (英語). NIST (2020年9月29日). 2022年2月16日閲覧。
(六)^ abFortier, Tara; Baumann, Esther (2019-12-06). “20 years of developments in optical frequency comb technology and applications” (英語). Communications Physics 2 (1): 153. arXiv:1909.05384. Bibcode: 2019CmPhy...2..153F. doi:10.1038/s42005-019-0249-y. ISSN 2399-3650.
(七)^ abW.H. Oskay (2006). “Single-atom optical clock with high accuracy”. Physical Review Letters 97 (2): 020801. Bibcode: 2006PhRvL..97b0801O. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.020801. PMID 16907426. オリジナルの2007-04-17時点におけるアーカイブ。.
(八)^ Fritz Riehle. “On Secondary Representations of the Second”. Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, Division Optics. 2015年6月23日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2015年6月22日閲覧。
(九)^ ab“The most accurate clock ever made runs on quantum gas” (英語). Wired UK. ISSN 1357-0978 2022年2月11日閲覧。.
(十)^ Schmittberger, Bonnie L. (21 April 2020). "A Review of Contemporary Atomic Frequency Standards". p. 13. arXiv:2004.09987 [physics.atom-ph]。
(11)^ Golovizin, A.; Tregubov, D.; Mishin, D.; Provorchenko, D.; Kolachevsky, N.; Kolachevsky, N. (2021-10-25). “Compact magneto-optical trap of thulium atoms for a transportable optical clock” (英語). Optics Express 29 (22): 36734–36744. Bibcode: 2021OExpr..2936734G. doi:10.1364/OE.435105. ISSN 1094-4087. PMID 34809077.
(12)^ “171Ytterbium BIPM document”. 2015年6月27日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2015年6月26日閲覧。
(13)^ “PTB Time and Frequency Department 4.4”. 2017年11月7日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2017年11月3日閲覧。
(14)^ “PTB Optical nuclear spectroscopy of 229Th”. 2017年11月7日時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。2017年11月3日閲覧。
(15)^ Norton, Quinn. “How Super-Precise Atomic Clocks Will Change the World in a Decade” (英語). Wired. ISSN 1059-1028 2022年2月15日閲覧。.
(16)^ [https://www.japan-acad.go.jp/japanese/news/2015/031201.html 2015年度日本学士院賞﹁光格子時計の発明とその開発﹂
(17)^ 東京大学香取研究室の研究テーマ
(18)^ H. Katori, M. Takamoto, V. G. Pal'chikov, V. D. Ovsiannikov, Ultrastable optical clock with neutral atoms in an engineered light shift trap, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 173005.
(19)^ M. Takamoto, F. L. Hong, R. Higashi, H. Katori, An optical lattice clock, Nature 2005, 435, 321.
(20)^ 産総研計量標準報告 Vol.4, No.3 光格子時計を用いた光周波数標準
(21)^ 応用物理、第74巻、第6号︵2005︶
(22)^ 情報通信研究機構 > 新世代ネットワーク研究センター > 光・時空標準グループ > 次世代時刻周波数標準プロジェクト > 研究紹介 >Sr光格子時計>ストロンチウム︵Sr︶原子を用いた光格子時計の研究開発
(23)^ 論文受理は2013年10月25日付け
(24)^ 東大、原子時計より高精度な﹁光格子時計﹂に必要な技術を開発 財経新聞 2014年6月24日
(25)^ Lamb-Dicke spectroscopy of atoms in a hollow-core photonic crystal fibreNature Communications 5, Article number: 4096 doi:10.1038/ncomms5096
(26)^ 共同発表‥次世代時間標準﹁光格子時計﹂の高精度化に成功〜2台の時計が宇宙年齢138億年で1秒も狂わない再現性を実証 2015年2月10日 科学技術振興機構︵JST︶東京大学 大学院工学系研究科 理化学研究所
(27)^ Cryogenic optical lattice clocksNature Photonics︵2015︶ doi:10.1038/nphoton.2015.5
(28)^ イッテルビウム光格子時計の開発に成功 産業技術総合研究所 2009年7月29日
(29)^ Applied Physics Express Vol.5︵2012︶ Article No:102401 "Improved Absolute Frequency Measurement of the 171Yb Optical Lattice Clock towards a Candidate for the Redefinition of the Second".
(30)^ イッテルビウム光格子時計が新しい秒の定義の候補に 産業技術総合研究所 2012年11月1日
(31)^ Smithsonian Institution Research Information Systemの記述
(32)^ 1949年7月に成立した特許の内容
(33)^ 計量単位令 別表第一 項番三、﹁秒﹂の欄
(34)^ イアン・カステロ=コルテス, ed (1996). ギネスブック'97. マイケル・フェルドマン. 騎虎書房. p. 162. ISBN 4-88693-605-9
(35)^ 6500万年にわずか1秒の誤差!光格子時計の精度を世界で初めて光ファイバで結び実証
(36)^ Applied Physics Express Vol.4︵2011︶ No.8 Article No:082203 “Direct Comparison of Distant Optical Lattice Clocks at the 10-16 Uncertainty”
(37)^ 6500万年に1秒しか狂わない時計 東大など精度実証 朝日新聞︵asahi.com︶・ 2011年8月5日付け掲載記事︽2014年2月6日閲覧→現在はインターネットアーカイブに残存︾
(38)^ “Google public NTP” (英語). Google. 2022年1月26日閲覧。 “We implemented Google Public NTP with our load balancers and our fleet of atomic clocks in data centers around the world.”

